
TECHNOLOGY
Generation II
LWGR ( Light Water Graphite Reactor)
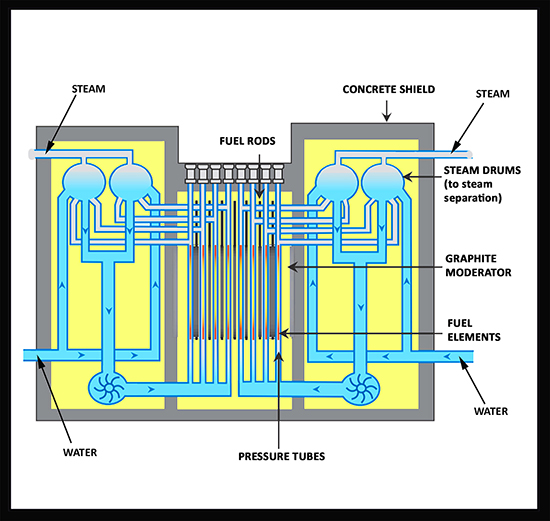
Source: "Power Reactors - Characteristics. 2010 WNA Pocket Guide", World Nuclear Association, July 2010 [25]
LWGR ( Light Water Graphite Reactor) is a group which representative construction is RBMK reactor - Reaktor Bolszoj Moszcznosti Kanalnyj. It is boiling water reactor, light water cooled and with graphite as moderator. This design was developed from army construction to pluton production. It is pressure tube and single circuit reactor. Steam is generated directly in the reactor and separated in steam drums (Fig. 17 ). Water used in RBMK is radioactively contaminated. Reactor should be shielded up as BWR is. As all tube reactors, RBMK is a large construction. It has vertical graphite blocks with fuel tubes. Mass of graphite is enormous so the core is heavy and power density is very low, only 5,8 MW/m3. Parameters of steam in the outlet of steam drums are average, 280 ºC and 6,38 MPa. Advantage of RBMK reactors is low fuel enrichment level and possibility to replace fuel tubes during reactor's operation (up to 5 replacements per day). However very high graphite temperature and positive reactivity factor makes RBMK reactors very dangerous. RBMK net efficiency is around of 31 %. It uses enriched fuel in uranium dioxide. An enrichment level is 2,6 - 2,8 % U-235. RBMK was a Soviet design, at the beginning assumed to be highly secure, because of very low power density in the core and possibility to control technology process separately in each tube - modular construction. As the history shown, mistakes in design and lack of elementary security systems led to one of the most serious nuclear disaster in the World. RBMK was not sold outside Soviet Union not only because dangerous construction but also because it can produce plutonium. ZSRR did not want to sell a technology to weapon production. [16],[21],[28]


-
Nuclear power industry|
Technology|
The electricity supply system aspect|
Economics|
Environment|
Public aspect|
Future|
Legislation|
References|