
TECHNOLOGY
Generation II
PHWR (Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor)
Source: "Power Reactors - Characteristics. 2010 WNA Pocket Guide", World Nuclear Association, July 2010 [25]
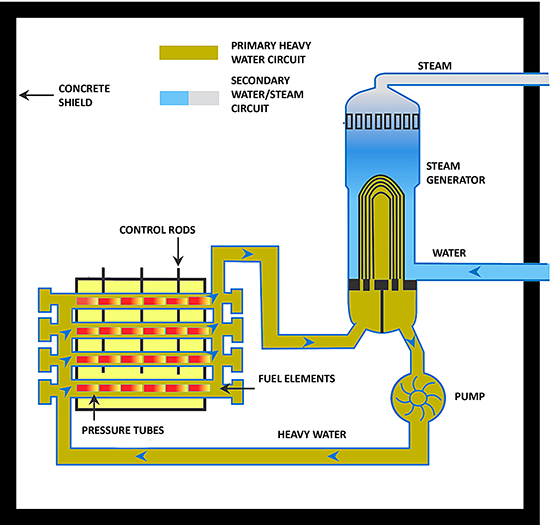
PHWR (Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor) is Canadian heavy water cooled and moderated reactor, commonly named as CANDU. Heavy water reactors are large constructions with the large core. Heavy water has not enough dissipation cross-section to ensure core dimensions like PWR or BWR. To slow down fast neutrons to thermal neutrons, much more heavy water is needed. Therefore construction with pressure vessel reactor can not be applied, and CANDU is a pressure tube reactor. The PHWR is double circuit reactor and it has pressurized primary circuit as PWR has. Pressure at level of 10 MPa, prevents water from boiling. Unfortunately water after being heated up in the core has not a high temperature. In the steam generator, steam produced has only 260 ºC at pressure of 4,7 MPa. It is the reason of very low efficiency. PHWR net efficiency is around of 28 % - the lowest among operating reactors. It uses natural fuel in metal uranium. The main advantage of PHWR reactors is ability to refuel taking place during normal operation. It increases availability of reactor. Additionally CANDU reactors are said to be the most secure constructions in the World today. Benefits from avoiding fuel enrichment process are significantly decreased with cost of heavy water separation. [16],[21],[24],[31]


-
Nuclear power industry|
Technology|
The electricity supply system aspect|
Economics|
Environment|
Public aspect|
Future|
Legislation|
References|