TIDAL POWER SYSTEMS
Tidal barrage
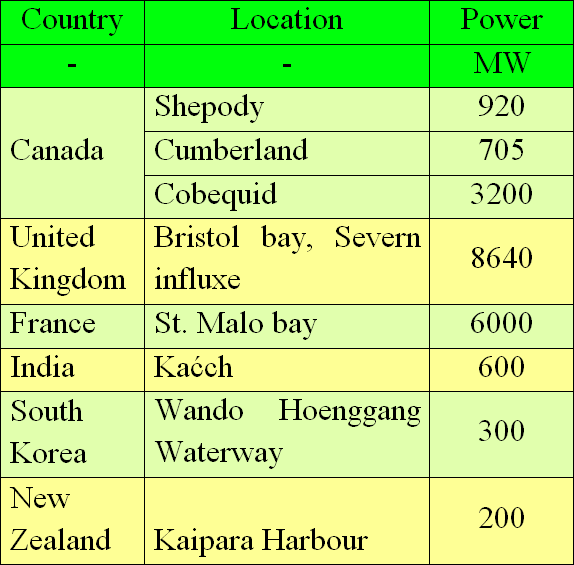
The most common tidal technology is barrage, mainly located near shores with high tidal movement, often on influxes or bays. This solution is similar to hydro power plants which are installed landlocked on the rivers. Usually the dam was one or more sluice to allow the ship traffic. In Rance (France), where is the largest tidal power plant in the world, the barrage wall is also a bridge on the Rance river (330 meters of length). The ducts are made inside the dam (the number of ducts depends from the barrage width) where the hydro-turbines are installed (usually bulb type turbines). Total the shaft connects the turbine with generator which are grouped for a few per power unit. The turbines are constructing on two way rotation, thus the power plant can works during high and low tide. (Fig.21)
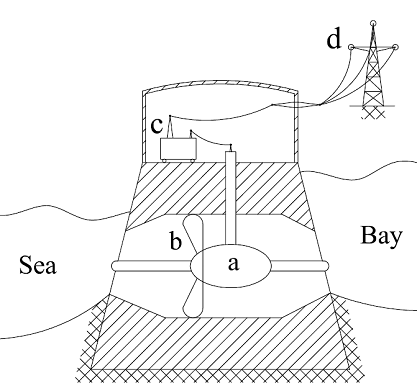
The dam is the main part of the tidal power plant and requires the largest part of total investment costs. Inside the dam wall are the ducks where the turbines are installed. The ducks concentrate the flow and creates the pressure difference. The turbine can works in horizontal or vertical position. In that method the turbine looks and works similar to the ship propeller (Fig. 21) and called the Kaplan turbine. The shaft connects the turbine with hydro-generator. Usually the hydro-turbines rotate with low rate thus the hydro-generator have more pole-pairs than typical generator. That design changes the dimension and shape. The hydro-generators are relatively short but with large diameter. The generator taps are connected with the transformer (by the cable) which transforms energy parameters and put the energy into electrical network. Often the Stralfo units are used in hydro power plants. The difference consists of the rotors pole installed on the hydro-turbines and the stators pole installed around the turbine. In that solution there is no diameter limitation what improves inertial moment and boosts steadiness and decreases vibrations.[10], [30] As opposed to the wind and solar technologies, the tidal barrage may operate almost whole day. The following chart shows the work cycle of Rence power plant. (Fig. 22)
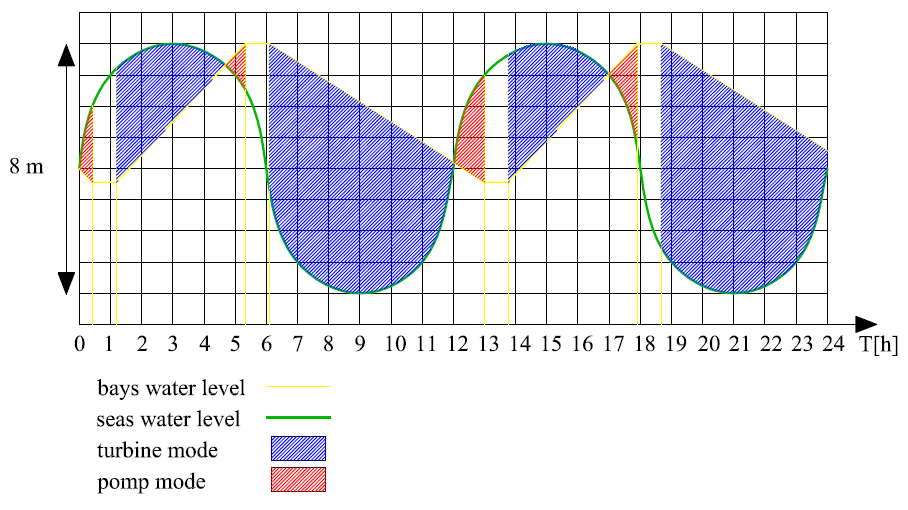
The curve of pomp mode increases faster than the turbine mode curve. Therefore the pomp mode improves the amount of gained energy. Moreover the turbine mode period during the low tide is longer than during the high tide because the Rence power plant is located in river influx which provides water to the bay. Duration of the turbine mode period is about 82% and the pomp mode 18%, thus the power plant can generate energy about 7200 hours annual. The quality of energy is high and easy to generate without expansive converters, because the tides are predictable. At present the Rence power plant is the largest in the world but in plans are also :(Fig. 23)[30], [31]
Tidal Stream Generator
The second one tidal technology is TSG – Tidal Stream Generator (also called Marine Current Turbines – the MCT). That technology consists in extracting energy from seas and oceans streams (currents). The TSG construction and energy conversion is similar to wind power plants. There are also two main types of them with turbine in horizontal and vertical position. Obviously the water celerity is much lower than the air but the water density is 832 times higher than the air. The power is also express similar to the air (2.3), (2.18): [33]
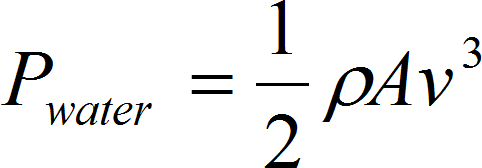
where: ρ – air density A – area swept by the rotating blades v – wind speed If the A of water turbine equals A of wind turbines, then:
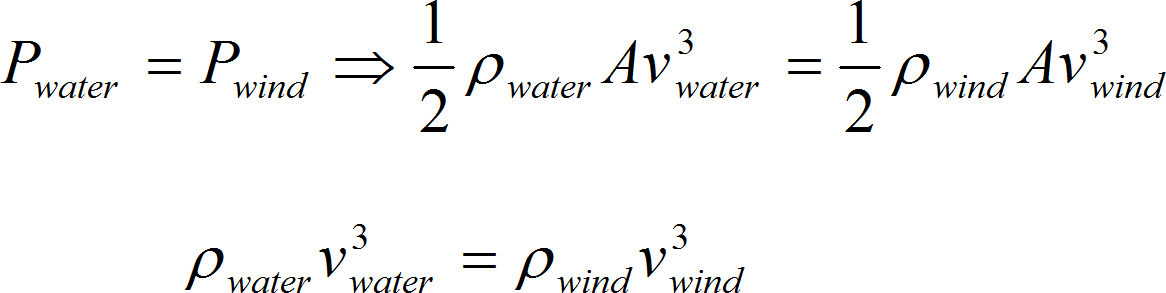
and if the water density is 832 times higher than the wind:
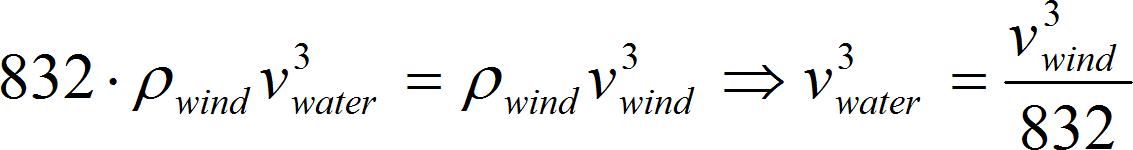
then finally:
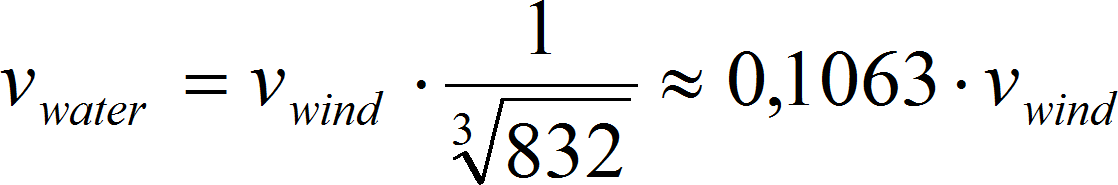
It is easy to see that the water turbine can obtain similar amount of energy from the water current with 1 m/s velocity than the wind turbine with the same swept area from the wind with 10 m/s velocity. Although the TSG are similar to wind turbines, however the construction has to be more massive due to higher density, e.g. the hub has larger diameter and the blades are shorter and wider. The devices are constructed on the shallows, not deeper than 30 meters. Moreover the turbine should be located about 5 meters under the water surface and about 5 meters over the seabed. Typical size of the turbine diameters is between 5 and 15 meters. The rotor blades rotate slowly about from 10 to 15 times per minute. The main part is the tubular tower (monopole) upon which the one or two horizontal axis turbines are installed. Inside the nacelle the gear box and the generator are installed. In similar way like in wind technology case. [33], [34] The vertical axis technology extracts the energy in the same way like horizontal axis devices, however they can be construct in two way: directly upon the floor or under the buoy. Both technologies are relatively new and still in research stage. Moreover the efficient of vertical axis turbine is relatively low. However the UK government supply the support for the TSG development. [33]
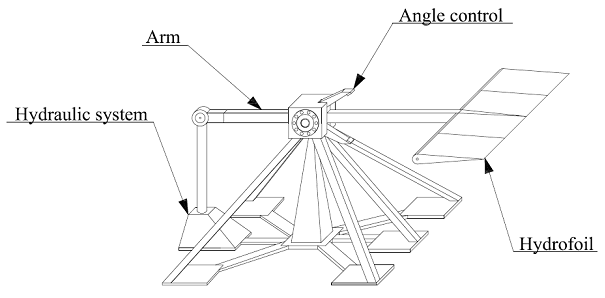
At present most of the TSG power plants are in experimental stage, e.g. “Seaflow”. The Seaflow is a test system consists of single horizontal axis turbine installed onto tubular tower located in Devon. It is one of the first constructed the TSG. The nominal turbine power equals 300kW. In April 2008 the second one prototype called SeaGen (constructed by the Marine Current Turbines - MCT) has been constructed in Strangford Lough in Northern Ireland. It is a twin horizontal axis turbines with total nominal power equals 1,2MW. That turbine can generate 10MWh of energy per tide and 6000MWh annual. The MCT has in plan to construct a power plant consist of 7 SeaGen type turbines, each 1,5MW of power (10,5MW of total power), in 25 meters deep. [30], [32], [34] The Oscillating Hydrofoil Generator (OHG) is the next one oceans streams technology. That technology has simple construction and in the same way is relative inexpensive. The OHG is located on the seabed but no deeper than 30 meters. That system consists of the hydrofoil attached to an oscillating lever which is connected with a hydraulic system (Fig. 25). The hydrofoil and the arm may by installed in horizontal or vertical position. Then the arm works similar to a whale (for the vertical position) or a shark (for the horizontal position) fin. Under the tidal current influence the arm motions and drives fluid. The fluid flows in closed cycle and drive a hydraulic motor which is connected with generator. The angle control provides continuous and smooth work (angle limitation is about 35°). [35]
The last one stream generator uses the Venturi Effect. That generator is installed in the ducts. The duct input and output has wider diameter than the rotor. When the water flow into the duck, the structure of it concentrate the stream. That provides to the pressure difference between input and output. That difference can be used to obtain the energy in two ways. The first method consists in the horizontal axis turbine installed in the narrowing. The turbine works similar to previously described generator however the pressure difference improves their efficiency by the power density increase and the flow acceleration. The second method use the pressure difference to create water level dissimilarity, which can be use to drives hydraulic system. (Fig. 26) [30], [32], [35]
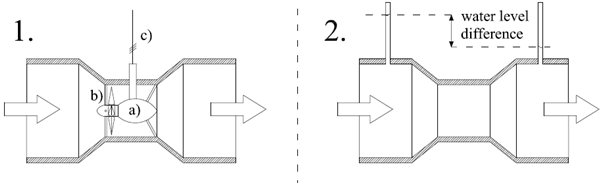
The Tidal In Stream is the one of the devices which is related with both technologies – horizontal axis turbine installed inside the duct concentrator. Above mentioned technologies are the most common of the TSG, however they are still in research stage. The most commercialised is single and twin rotor generator with horizontal axis turbines. Most of devices which extract energy from tides are installed on the seabed. There are a few ways to do it:
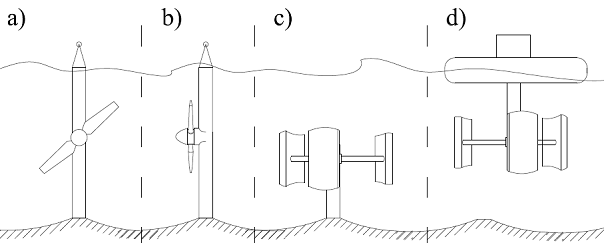
- The first one method calls seabed mounted or gravity base. This is simply attached the TSG to the floor. It is the most common solution for technologies like vertical axis turbines or hydrofoil generators, [30], [35]
- The pile mounted method is more expansive but for a horizontal axis turbines more useful. Device is attached to a pole penetrating the seabed. The second end of pile is above the water level, where the transformer and necessary apparatus are installed. Often turbines are attached to the mechanism allows to rise the turbine over the water for maintenance. [30], [35]
- Next methods consist on the floating buoy upon the water surface with submerged generator. That solution is used with vertical axis turbine technologies. It can be realized in three ways. The buoy with device is fixed to the sea bead by the cable (Flexible mooring). Also the device is connected with mooring system which holds it in specific position (Rigid mooring). Finally, several devices can be mounted on a single platform, which moves with water level changes, [30], [35]
- The last one method (Hydrofoil Inducting Downforce) is for hydrofoil generators. Several devices are installed on a frame, [30], [35]
-
Description of technology|
Economic aspects|
Environment and public awareness|
Legislation|
Final comparison|
References