
WIND POWER
Wind is a movement of air on the surface of earth. Sunbeams heats the earth irregular, what create atmospheric pressure differences, between which the air moves and makes the wind. Irregular heating is due to angle of sunbeam radiation, type of heating surface (water, soil, rocks, and sands), level of clouded, terrain configuration, elevation, and day cycle. However the Sun is not only one reason of wind. There are also the Coriolis force, in global meaning and many local factors such as e.g. mountainous terrain surface or forest areas. Below picture depict exemplary temperature levels of air on the earth.
As we can see there are many factors which have influence on wind direction and speed. But despite all of these factors, humanity is familiar whit that appearance and can demarcate some of characteristic types of wind. It is: blasts, daily wind speed changes and frontal system moves. The shortest period of time is telltale for blasts. Duration of that blowing is between a few and several seconds, for example from 10 to 70 seconds. Beside the duration, blasts have also high speed and carry large mass of air. That appearance is not desirable because considerable and temporary changes of wind speed have strong influence on speed of wind power turbine rotation what may effect the power generation and voltage fluctuations. Much slower and less tempestuous appearance is called daily wind speed changes. It is related to heating air during the day and cooling at night. That is why the wind blows during the day and at night not. A period of this cycle is 24 hours. The longest time of duration is characteristic for frontal system moves with nearly few days period. For wind energetic the most important are daily, annual and perennial wind speed changes. In planning stage a main factors are this three wind speed profiles which have influence on the localization of wind power plants. The map below shows, where in Europe the strongest wind blows.
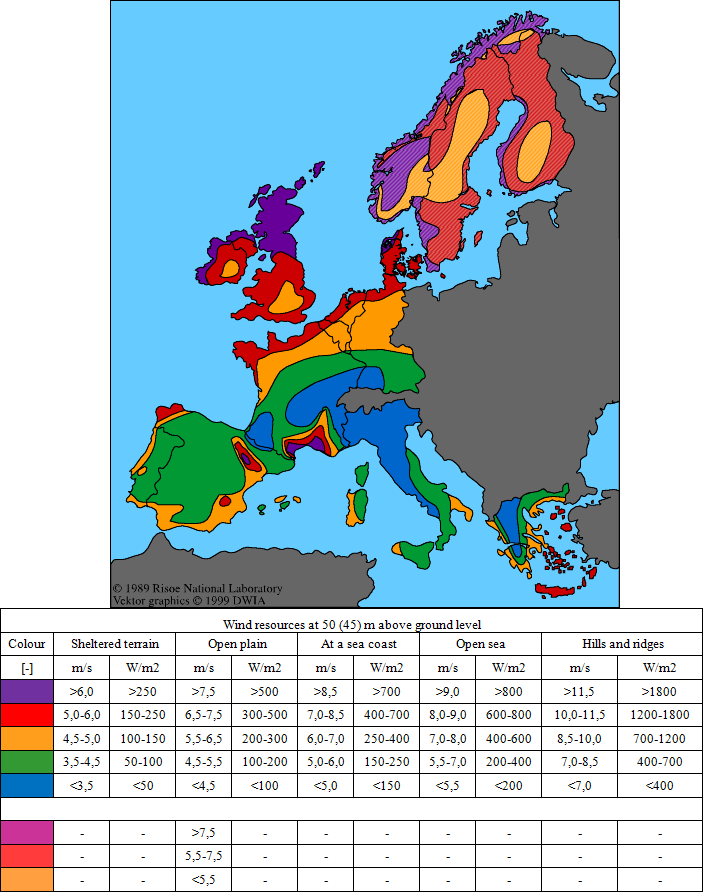
Source: Danish Wind Industry Association: www.windpower.org
For the EU technical potential allow to obtain 120 to 180 GWe in 2020 and from 168 to 300 GWe in 2030.
-
Description of technology|
Economic aspects|
Environment and public awareness|
Legislation|
Final comparison|
References

