
ENVIRONMENT
Main mechanisms of nuclear power plant influence
Any impact on environment like on ground, air, surface water and ground water is strongly connected with people health. Almost every contamination affects human body at last. Only small part is in relation to climate or ecosystem. Figure no. 40, presented below, shows how wastes reach human's body.
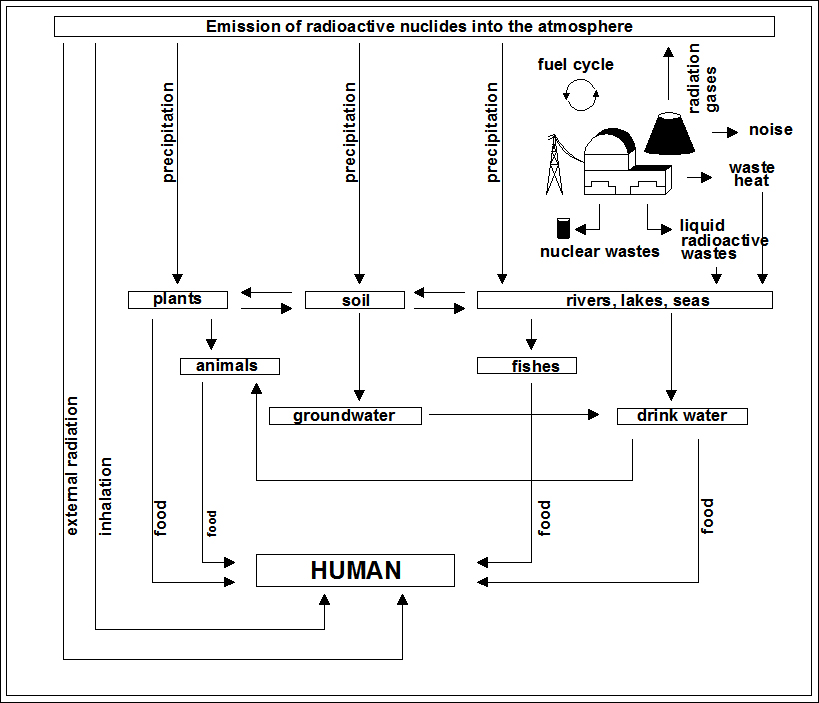
Source: Own development based on A. O z i e m s k I, "Energetyka a srodowisko" Materialy wykladowe., Instytyt Elektroenergetyki Wydzialu Elektrotechniki, Elektroniki, Informatyki i Automatyki Politechniki Lódzkiej, Lódz, academic semester: summer 2009/2010, [102] L. S z k u d l a r e k, D. L e w i c k a - S z c z e b a k, M. K a s p r z a k "Prognoza oddzialywania na srodowisko programu polskiej energetyki jadrowej", 2010, http://bip.mg.gov.pl/node/12331 , [103]
Nuclear power plant influences the environment by three main ways:
Radioactive nuclides are formed during fission reaction inside the reactor. However they are acting with all materials surrounding them. The vast majority of radioactive particles are effectively kept in the fuel and in the reactor, but small part of them, through the natural and caused by wear and erosion leaks get outside and penetrate into the environment. Nuclear wastes directly from the reactor core are also a problem but it has been presented in "Nuclear wastes storage options". Radioactivity in the material, caused by unstable atoms, is measured by Becquerel unit [Bq]. Unit refers to number of single nuclear disintegrations in the material per second. Value of 1 Bq, means one decay per second. This unit is not entirely clear. Two materials of the same radioactivity (using Becquerel unit), gives different radiation dose for someone who handles it. Radiation dose is additionally affected by half-life of disintegration products. Short-lived particles do not influence radioactivity, but they increase radiation dose. Such conditions, separated uranium and uranium ore present - ore consist short-lived particles, what lead to increase of received radiation dose. Examples of material's radioactivity: 1kg uranium - 25 MBq, 1 kg of coffee - 1 kBq, potassium-40 in milk - 40 Bq/kg, 1 kg of vitrified nuclear waste after 50 years - 10 TBq, 1 kg of low level wastes - LLW - 1 MBq. [102],[104]
-
Nuclear power industry|
Technology|
The electricity supply system aspect|
Economics|
Environment|
Public aspect|
Future|
Legislation|
References|

